-
 Lanyue Metal Technology
Lanyue Metal Technology
-
 [email protected]/[email protected]
[email protected]/[email protected]
-
 24 Hour Service - 7 Days a Week
24 Hour Service - 7 Days a Week

Industry News
Metal Rolling Bearings: A Comprehensive Analysis from Material Selection to Working Principles
Introduction
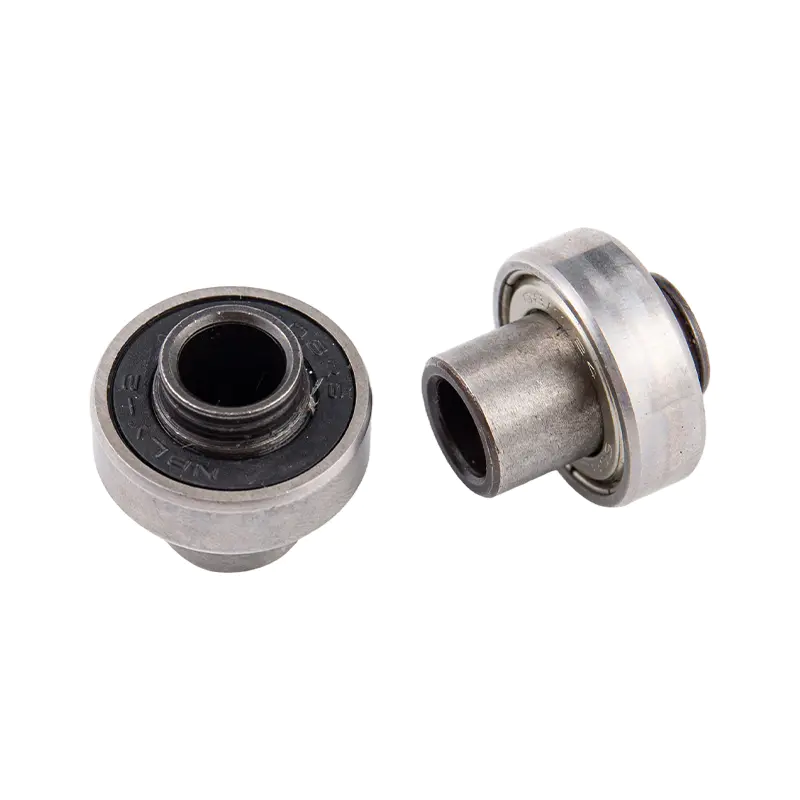
Metal rolling bearings (Metal Rolling Bearing) are crucial mechanical components widely used in modern industries. Whether in the automotive, aerospace, railway, wind energy, petrochemical, metallurgy, or other fields, rolling bearings play a vital role. They effectively reduce friction between mechanical parts, lower energy consumption, enhance operational efficiency, and extend the service life of equipment. With the continuous advancement of industrial technology, the requirements for metal rolling bearings have increased, particularly in terms of precision, durability, and working environment.
This article delves into various aspects of metal rolling bearings, including material selection, working principles, application fields, lubrication technologies, and how to enhance their performance and durability. Through a comprehensive analysis of these aspects, you will gain a better understanding of the important role that metal rolling bearings play in modern industries.
Part 1: Material Selection for Metal Rolling Bearings
1.1 Common Materials for Metal Rolling Bearings
The material selection for metal rolling bearings directly affects their performance and service life. Choosing the right material can not only improve the bearing's load-bearing capacity but also make it perform more stably in different working environments. Common materials for metal rolling bearings include high-carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, and ceramics.
1.1.1 High-Carbon Steel
High-carbon steel is the most commonly used material for metal rolling bearings. It offers good wear resistance, hardness, and fatigue resistance. Its carbon content usually ranges from 0.8% to 1.0%, and heat treatment (such as quenching) can be used to increase its hardness, making the bearing surface more wear-resistant. The advantage of high-carbon steel is its relatively low cost, making it suitable for most general industrial applications. However, its performance may not match other alloy steels under high-temperature, high-speed, or harsh environments.
1.1.2 Alloy Steel
Alloy steel is a material that improves the performance of steel by adding various alloying elements such as chromium, molybdenum, and vanadium. Bearings made from alloy steel offer significant advantages in wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and fatigue resistance, especially in high-load and high-speed operating conditions. Common alloy steels such as 52100 steel are widely used in aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery industries.
1.1.3 Stainless Steel
Stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance and is suitable for rolling bearings in high-humidity or corrosive environments. Bearings made from stainless steel are usually made from materials such as 304 or 440C stainless steel, offering high oxidation and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for food processing, medical equipment, and chemical industries. Although the hardness and wear resistance of stainless steel bearings are slightly lower than those of alloy steel, their performance in harsh environments is exceptional.
1.1.4 Ceramic Materials
Ceramic bearings are typically made from materials like alumina, silicon nitride, or boron nitride. They offer extremely high hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. Ceramic materials have a lower density, which reduces the weight of the bearings, making them suitable for high-speed and high-precision applications. Ceramic bearings are commonly used in aerospace, medical devices, and precision instruments. However, the cost of ceramic bearings is higher, and they are more brittle, requiring precise installation and maintenance.
1.2 Factors Affecting Material Selection
The selection of materials for bearings is not just about cost; it also depends on the actual working conditions. Here are some key factors to consider:
1.2.1 Load-Bearing Capacity
The load-bearing capacity of a bearing directly affects its service life. Bearings that are subjected to excessive loads over long periods will experience accelerated wear and fatigue, leading to performance degradation. To enhance the durability of bearings, it is essential to ensure they operate within their rated load range and avoid overloading.
1.2.2 Environmental Conditions
The working environment of the bearing is a key factor in material selection. Bearings operating in high temperatures, high humidity, or corrosive environments require materials with good temperature resistance and corrosion resistance. In these environments, stainless steel and ceramic materials are often more suitable than regular steel.
1.2.3 Operating Speed
The operating speed of a bearing is closely related to the friction characteristics of the material. Bearings operating at high speeds require materials with low friction coefficients, such as ceramics, to significantly reduce energy loss and heat generation. Alloy steel bearings perform better at medium to high speeds.
1.2.4 Cost and Economy
Cost is a crucial factor in material selection for many general industrial applications. High-carbon steel bearings, although less effective than alloy steel or stainless steel bearings, are more cost-effective and are suitable for low-load and standard environmental conditions.
Part 2: Application Areas of Metal Rolling Bearings
2.1 Automotive Industry
In automotive manufacturing, rolling bearings are used in key components such as engines, transmissions, wheels, and suspension systems. Automotive bearings must withstand high speeds, high temperatures, and heavy loads, making alloy steel or ceramic bearings the preferred choice. Particularly in high-speed driving, heavy loads, and frequent stop-and-go situations, the quality of automotive bearings is critical to overall vehicle performance.
2.2 Aerospace
The aerospace industry has extremely stringent requirements for bearings, especially in high-speed, high-pressure, and high-temperature environments. Bearings made from ceramic or alloy steel are used in critical components such as jet engines and flight control systems. The key factors in material selection for aerospace bearings are weight, high-temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance.
2.3 Machinery Manufacturing
In the machinery manufacturing industry, metal rolling bearings are used in equipment such as machine tools, heavy machinery, and compressors to reduce friction and enhance efficiency. These machines often operate under high loads, and bearing strength and wear resistance are crucial. Alloy steel bearings are commonly selected for such applications.
2.4 Wind Power
Wind turbines operate in complex environments, and the bearings used in these systems must endure fluctuations in wind load, load changes, and adverse weather conditions. To improve durability and stability, bearings in wind power generators typically use stainless steel or alloy steel materials. These bearings require excellent corrosion resistance and long service life with minimal maintenance costs.
2.5 Railway and Urban Rail Transit
The safety and stability of railway and urban rail transit systems rely heavily on the quality of rolling bearings. Bearings used in rail transport must endure enormous loads, extended periods of use, and complex operating conditions. Alloy steel and stainless steel bearings are widely used in train axles, chassis, and other critical parts to ensure efficient and safe operation.
Part 3: Lubrication Technology and Performance Enhancement
3.1 The Necessity of Lubrication for Bearings
Lubrication is vital for the performance of metal rolling bearings. It reduces friction, minimizes wear, prevents corrosion, and aids in heat dissipation. Without adequate lubrication, bearings may suffer from excessive heat generation, leading to failure. Improper lubrication can also increase friction, resulting in power loss and decreased performance.
3.2 Lubrication Methods
3.2.1 Oil Lubrication
Oil lubrication is the most common method, suitable for high-temperature, high-load, and high-speed conditions. Oil lubrication forms a film on the bearing surface, effectively isolating metal surfaces and reducing friction and wear. Common lubricating oils include mineral oils and synthetic oils.
3.2.2 Grease Lubrication
Grease lubrication is used for medium-to-low-speed and low-load conditions. Grease forms a more stable lubrication film inside the bearing, reducing wear. Grease lubrication is preferred for long-term operations and situations where periodic maintenance is not possible.
3.3 Choosing the Right Lubricant
When selecting a lubricant, it is important to consider the type of lubricant (oil or grease) as well as its performance characteristics, based on the bearing's application environment, operating conditions, and lubrication requirements.
3.3.1 Viscosity
The viscosity of the lubricant directly affects the bearing’s lubrication performance. High-viscosity lubricants are typically used in high-temperature or high-load conditions. However, in low-temperature environments, excessively high viscosity can hinder the lubricant's flow, reducing its effectiveness.
3.3.2 Additives
Lubricating oils or greases often contain additives to improve their performance and extend service life. Common additives include antioxidants, anti-wear agents, and corrosion inhibitors. Selecting the right additives can significantly enhance bearing performance, preventing wear, corrosion, and oxidation.
3.3.3 Environmental Compatibility
For bearings operating in harsh environments such as high moisture, contamination, or corrosive conditions, the environmental compatibility of the lubricant is crucial. In these conditions, lubricants with corrosion-resistant and water-repellent properties are typically used. Additionally, the environmental impact of the lubricant is becoming an increasingly important consideration for many companies.
3.4 Consequences of Improper Lubrication
Improper lubrication is a leading cause of bearing damage and equipment failure. Common lubrication problems include insufficient lubrication, excessive grease, and degraded lubricants.
3.4.1 High Temperature
If lubrication is insufficient, excessive friction will generate heat, causing the bearing’s temperature to rise. High temperatures can accelerate the oxidation of lubricants and cause bearing materials to soften, resulting in wear and deformation, ultimately leading to bearing failure.
3.4.2 Corrosion and Rust
Without proper lubrication, the metal surfaces of bearings may be exposed to air and moisture, leading to oxidation and corrosion. This is particularly problematic in humid or corrosive environments. Corrosion not only affects bearing performance but may also result in complete bearing failure and significant damage to the equipment.
3.4.3 Wear and Failure
Improper lubrication can cause excessive wear on bearings. Long-term friction will damage the bearing surface, impacting its operational precision, increasing failure rates, and resulting in vibrations and noise. In high-speed operations, wear can lead to increased bearing clearance and operational instability.
3.5 Lubrication Tips to Enhance Bearing Performance
To improve the performance and extend the life of metal rolling bearings, it is essential to choose the right lubricants, perform precise installations, and maintain regular lubrication.
3.5.1 Regularly Inspect and Replace Lubricants
Regularly check the quality of lubricants to ensure their viscosity and lubrication performance are within acceptable ranges. Particularly under high-load or high-temperature conditions, the performance of lubricants will degrade over time. Therefore, replacing lubricants regularly is essential to maintaining bearing stability.
3.5.2 Use Appropriate Lubrication Systems
For heavy-duty and high-speed applications, it is recommended to use automatic lubrication systems. These systems continuously supply oil or grease to the bearing during operation, ensuring stable lubrication and reducing human error in lubrication.
3.5.3 Avoid Over-lubrication
While lubrication is crucial, over-lubrication can cause problems. Excess grease may increase friction inside the bearing, causing overheating and grease overflow. Therefore, it is important to ensure that the amount and type of lubricant match the working conditions.
Part 4: Durability Analysis of Metal Rolling Bearings
4.1 Main Factors Affecting the Durability of Metal Rolling Bearings
The durability of metal rolling bearings is influenced by various factors, including the following:
4.1.1 Material Properties
Material selection is one of the most crucial factors in bearing durability. High-quality materials can significantly enhance the bearing's resistance to fatigue, wear, and corrosion, extending its service life. Proper heat treatment techniques (such as quenching and tempering) can further improve the hardness and strength of materials, resulting in a more durable bearing.
4.1.2 Load
The load that the bearing is subjected to directly impacts its service life. Bearings that operate under overload conditions will experience accelerated wear and fatigue, leading to performance degradation. To improve the bearing's durability, it is crucial to ensure that the bearing operates within its rated load range and avoid overloading.
4.1.3 Operating Speed
High-speed operations generate more friction and heat, accelerating wear. Bearings running at high speeds will experience higher surface temperatures, and the choice of material and lubrication technology becomes more critical in such applications. Incorrect lubrication can lead to the bearing's aging faster than in low-speed conditions.
4.1.4 Working Environment
The working environment is another key factor that affects the durability of bearings. Bearings operating in high temperatures, low temperatures, moisture, or corrosive environments may experience material degradation and performance loss over time. Therefore, selecting bearings made from suitable materials and ensuring proper lubrication is critical for ensuring durability.
4.1.5 Installation and Maintenance
Improper installation and maintenance are common causes of premature bearing failure. Installation accuracy, matching tolerances, and lubricant quality and quantity all affect bearing durability. Regular inspections and maintenance can significantly extend bearing service life.
4.2 Strategies to Improve Durability of Metal Rolling Bearings
To improve the durability of metal rolling bearings, it is essential to adopt the following strategies:
4.2.1 Select High-Quality Materials
Choosing high-quality materials that are suitable for the working environment and load requirements is the first step in improving bearing durability. Bearings made from alloy steel, stainless steel, and ceramic materials can significantly improve fatigue resistance, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance, resulting in extended service life.
4.2.2 Precision Installation and Alignment
Installation accuracy is crucial for bearing durability. Improper installation or misalignment can cause excessive lateral loads on the bearing, increasing wear and fatigue. Therefore, bearings must be installed according to specifications and aligned with high precision.
4.2.3 Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Regular inspections of the bearing's lubrication status, operating temperature, and noise levels are essential to detect potential issues. Timely lubricant replacement and adjustment of the lubricant type and quantity based on operational conditions will help to maintain bearing durability. Regular cleaning and protection from contaminants are also essential to prolong bearing life.
Part 5: Working Principles of Metal Rolling Bearings
5.1 The Role of Rolling Elements
The rolling elements are the core components of metal rolling bearings, usually made of steel balls, rollers, or rings. The rolling elements reduce friction by rolling instead of sliding, greatly reducing the coefficient of friction and thus lowering energy loss and heat generation.
5.2 Inner and Outer Rings
Metal rolling bearings consist of inner and outer rings, rolling elements, and a cage. The inner ring is fixed to the shaft, while the outer ring is fixed to the housing. The rolling elements roll between the inner and outer rings, facilitating motion. The cage holds the rolling elements in place, preventing them from making direct contact with each other.
5.3 Load Distribution and Mechanical Analysis
During operation, the load applied to the bearing is evenly distributed across the rolling elements. The contact angle between the rolling elements and the inner and outer rings determines the bearing's load capacity. When the load exceeds the rated value, the contact area increases, generating more friction and heat, which affects the bearing's durability.
5.4 Comparison of Rolling Bearings and Sliding Bearings
Compared to sliding bearings, rolling bearings have advantages such as lower friction, higher efficiency, and longer service life. Rolling bearings reduce friction by rolling elements, while sliding bearings generate friction through sliding contact, leading to lower efficiency and increased wear. However, sliding bearings are still preferred in some high-load or low-speed applications.
Conclusion
Metal rolling bearings play an irreplaceable role in modern industries. Whether it is material selection, lubrication technology, durability analysis, or understanding the working principles, all directly impact bearing performance and service life. By selecting the right materials, ensuring precise installation, and maintaining regular lubrication, it is possible to significantly improve bearing efficiency and longevity, thus enhancing the overall stability and productivity of mechanical systems.
As a crucial component of industrial infrastructure, the continuous progress and optimization of metal rolling bearing technology will bring more efficient, energy-saving, and reliable operational experiences to various industries. We hope this article serves as a valuable reference for you when selecting and applying metal rolling bearings.
News categories
Exhibition Information
Product categories
Related Products
Contact
 1st Floor, Building 4, East Side, Jinger Road, Yuxin Town, Nanhu District, Jiaxing City, Zhejiang Province, China
1st Floor, Building 4, East Side, Jinger Road, Yuxin Town, Nanhu District, Jiaxing City, Zhejiang Province, China
 [email protected][email protected]
[email protected][email protected]
 +86-137 0583 8919+86-135 8638 0656
+86-137 0583 8919+86-135 8638 0656
Copyright © Jiaxing Lanyue Metal Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Custom High-Performance Industrial Fasteners Manufacturers, Suppliers
 English
English  Español
Español  Deutsch
Deutsch