-
 Lanyue Metal Technology
Lanyue Metal Technology
-
 [email protected]/[email protected]
[email protected]/[email protected]
-
 24 Hour Service - 7 Days a Week
24 Hour Service - 7 Days a Week

Industry News
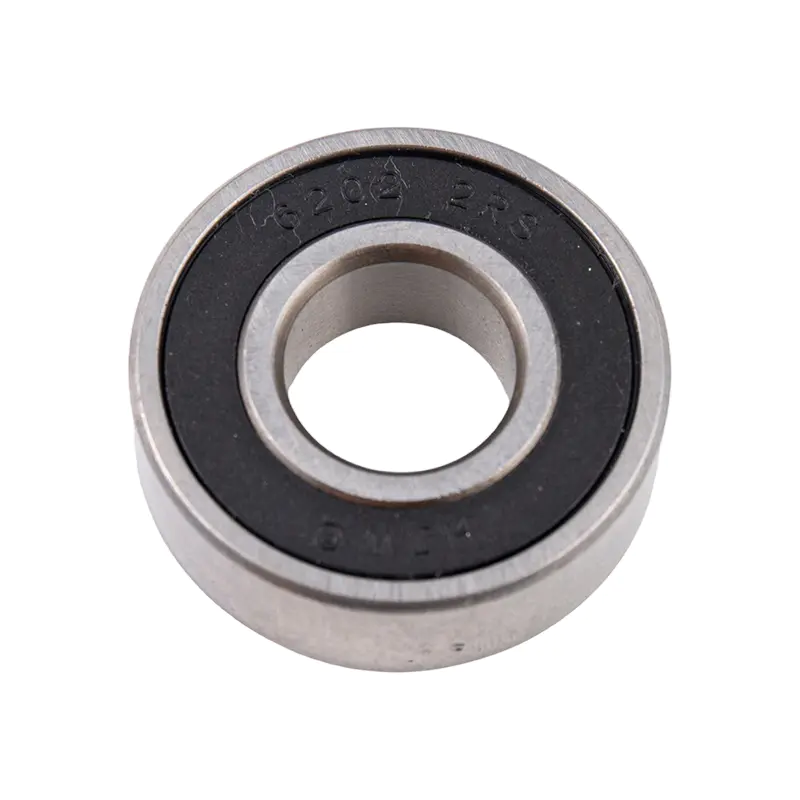
Which Types of Metal Rolling Bearings Suit Your Applications?
In today’s industrial landscape, the demand for high-performance metal rolling bearing is rapidly increasing across a wide range of sectors, from automotive and industrial machinery to renewable energy and robotics. These components play a crucial role in reducing friction, supporting loads, and enabling the smooth operation of rotating machinery. As industries continue to push for higher efficiency, precision, and durability, the importance of reliable metal rolling bearing has never been greater.
Basics of Metal Rolling Bearing
A metal rolling bearing is a component that supports and guides rotating or oscillating shafts while reducing friction using rolling elements like balls or rollers. Compared to plain bearings, they enable higher speeds, greater precision, and longer service life.
Common types include:
- Ball bearings – high speed, moderate loads.
- Roller bearings – heavy radial loads.
- Angular contact bearings – combined radial and axial loads.
- Tapered roller bearings – high radial and axial loads.
- Spherical roller bearings – handle misalignment and heavy loads.
Comparison of Common Metal Rolling Bearing Types
| Bearing Type | Load Capacity | Speed Range | Typical Applications | Advantages & Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ball bearing | Medium | High | Motors, precision instruments | High-speed capability, limited load capacity |
| Roller bearing | High | Medium | Heavy machinery | High load capacity, speed limited |
| Angular contact bearing | Medium–High | High | Machine tools, aerospace | Handles axial load, more expensive |
| Tapered roller bearing | High | Medium | Automotive hubs, heavy machinery | High radial load, moderate axial load |
| Spherical roller bearing | High | Medium | Wind turbines, mining | Accommodates misalignment, higher cost |
These basic categories form the foundation of most metal rolling bearing applications, and understanding their characteristics is essential for selecting the right bearing for any industrial or engineering project.
Materials and Manufacturing of Metal Rolling Bearing
The performance and longevity of a metal rolling bearing largely depend on the materials used in its construction. Bearing steel, such as AISI 52100, is the most common choice for high-precision rolling bearings due to its excellent hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength. For applications requiring corrosion resistance, stainless steel bearings are preferred, particularly in medical devices, food processing equipment, or marine environments. Alloy steels are also widely used for heavy-load applications, offering a balance between strength, toughness, and cost-effectiveness.
Manufacturing processes play a critical role in ensuring the quality and reliability of metal rolling bearing. The process typically begins with precision forging or turning of bearing rings, followed by heat treatment to achieve optimal hardness and durability. Grinding and lapping operations are then performed to achieve precise dimensional tolerances and smooth surface finishes. Advanced manufacturing techniques, including computer numerical control (CNC) machining and surface coatings, are increasingly employed to enhance bearing performance and longevity.
Common Materials for Metal Rolling Bearing
| Material Type | Hardness | Wear Resistance | Corrosion Resistance | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 52100 Bearing Steel | High | High | Moderate | High-precision ball bearings |
| Stainless Steel | Medium | Medium | High | Medical devices, corrosive environments |
| Alloy Steel | High | High | Moderate | Heavy machinery, industrial applications |
Selecting the appropriate material and manufacturing method is critical to ensuring that a metal rolling bearing can meet specific operational requirements, whether it is high-speed performance, heavy-load capacity, or resistance to harsh environments.
Performance Parameters and Applications of Metal Rolling Bearing
Key Performance Factors of a Metal Rolling Bearing
-
Load Capacity
- Determines how much radial and axial load a bearing can handle.
- Bearings with high radial capacity are ideal for heavy machinery.
- Bearings designed for axial loads perform well in high-speed or precision applications.
- Some bearings are engineered to manage combined radial and axial loads, providing versatile solutions for complex systems.
-
Speed Capability
- Indicates the maximum operational speed a bearing can safely sustain.
- High-speed applications often require specialized bearing designs to maintain efficiency and prevent overheating.
-
Lubrication Requirements
-
Essential for reducing friction, minimizing heat, and extending service life.
-
Common lubrication types include:
- Oil lubrication
- Grease lubrication
- Solid lubrication
-
The choice depends on operating conditions such as speed, temperature, and load.
-
-
Service Life and Maintenance
- Longevity can be affected by the operating environment, load fluctuations, and misalignment.
- Regular inspection, proper lubrication, and timely maintenance help prevent premature failures and ensure consistent performance.
Comparison of Metal Rolling Bearing Functional Features
| Feature | Description | Suitable Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Load capacity | Ability to withstand radial and axial loads | Industrial machinery, construction equipment | Ensures stability and reliability under heavy loads |
| Speed capability | Maximum operational rotational speed | Motors, turbines, precision instruments | Supports high-speed operation without excessive wear |
| Lubrication type | Oil, grease, or solid lubrication | High-speed equipment, harsh environments | Reduces friction, prevents overheating, extends service life |
| Misalignment tolerance | Ability to function under shaft or housing misalignment | Wind turbines, mining equipment | Maintains performance despite installation or operational deviations |
| Durability | Lifespan under typical operating conditions | All industrial applications | Reduces downtime and maintenance costs |
By analyzing these functional features, engineers and procurement specialists can select metal rolling bearing that meets the precise requirements of their machinery, ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and efficiency.
Key Functions of Rolling Bearings in Mechanical Systems
Rolling bearings play a crucial role in ensuring smooth operation and efficiency in mechanical systems. Their functions can be understood from several perspectives, ranging from friction reduction to load management and precision maintenance. Below are the main functions:
Friction Reduction and Energy Efficiency
One of the primary functions of rolling bearings is to reduce friction between moving parts. Unlike plain bearings that rely on sliding motion, rolling bearings employ rolling elements such as balls or rollers to carry the load. This rolling motion significantly lowers the coefficient of friction, leading to:
- Reduced energy consumption in motors and machinery.
- Lower operating temperatures due to less heat generation.
- Improved performance in high-speed applications, as rolling friction is more manageable than sliding friction.
Load Support and Distribution
Rolling bearings are designed to support different types of loads, including radial, axial, and combined loads. The type and shape of rolling elements determine the load capacity and distribution characteristics. For instance:
- Ball bearings: Best suited for moderate radial and axial loads, providing smooth operation at high speeds.
- Roller bearings: Can handle heavier radial loads due to the larger contact area between the rollers and raceways.
- Tapered roller bearings: Designed to carry combined loads, effectively distributing axial and radial forces simultaneously.
Vibration and Noise Reduction
High-quality rolling bearings also help reduce vibration and noise in mechanical systems. The precision manufacturing of the bearing components ensures uniform rolling element movement, which leads to:
- Quieter operation in motors and appliances.
- Reduced wear and tear on adjacent components, increasing overall system lifespan.
- Enhanced stability in precision equipment such as machine tools and robotics.
Precision and Positioning Control
Many mechanical systems require precise rotational movement. Rolling bearings contribute to this by maintaining the alignment and positioning of shafts:
- High-precision angular contact bearings are widely used in CNC machines and aerospace applications.
- Deep groove ball bearings provide smooth rotation with minimal axial displacement.
- Tapered roller bearings maintain shaft positioning under heavy loads, ensuring consistent performance.
Comparison of Rolling Bearing Functions
| Function | Ball Bearings | Roller Bearings | Tapered Roller Bearings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Friction Reduction | High efficiency at moderate loads | Moderate efficiency under heavy loads | Moderate efficiency, good for combined loads |
| Load Capacity | Moderate radial and axial loads | High radial loads | High radial + axial loads |
| Noise & Vibration Control | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Precision & Positioning | Moderate to high | Moderate | High |
| Typical Applications | Motors, household appliances | Heavy machinery, conveyors | Automotive, gearboxes, aerospace |
Enhanced Functional Benefits in Practical Applications
The functional advantages of rolling bearings are not limited to theoretical performance—they translate into tangible benefits in real-world applications. Understanding these benefits helps in selecting the right bearing type for specific mechanical needs.
High-Speed Capability
Rolling bearings are engineered for high-speed operations. The rolling motion minimizes heat generation and wear, making them suitable for:
- Electric motors that operate continuously at high RPMs.
- Machine tools requiring precision at high spindle speeds.
- Automotive components, such as wheel hubs and transmission shafts, where high-speed rotation is common.
Load Adaptability and Durability
The ability of rolling bearings to handle varying loads is a major functional advantage. Depending on the design:
- Cylindrical roller bearings can manage heavy radial loads without deformation.
- Angular contact bearings maintain axial stability under thrust loads.
- Tapered bearings distribute both axial and radial forces efficiently, prolonging service life.
Maintenance Reduction
Rolling bearings are often designed for long operational lifespans with minimal maintenance:
- Pre-lubricated bearings reduce the need for frequent lubrication.
- Sealed bearings prevent contamination from dust and moisture, enhancing reliability.
- Lower wear rates reduce the risk of component failure, decreasing downtime and maintenance costs.
Versatility Across Industries
The functional attributes of rolling bearings make them indispensable in multiple industries:
- Automotive: Bearings ensure smooth wheel rotation, efficient engine operation, and stable transmission systems.
- Industrial machinery: Bearings support heavy machinery components, enabling reliable and continuous operation.
- Consumer electronics and appliances: Bearings provide quiet and smooth movement in fans, washing machines, and compressors.
- Aerospace: High-precision bearings allow for reliable performance under extreme conditions, including high speeds and variable loads.
Functional Benefits Across Applications
| Application Industry | Key Functional Requirement | Bearing Type Recommended | Benefit Provided |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Load handling, durability | Tapered roller bearings | Smooth rotation, long service life |
| Industrial Machinery | Heavy load, continuous operation | Cylindrical roller bearings | High radial load capacity, stability |
| Consumer Electronics | Low friction, quiet operation | Deep groove ball bearings | Reduced noise, energy efficiency |
| Aerospace | Precision, reliability | Angular contact ball bearings | High-speed rotation, accurate positioning |
The functionality of rolling bearings extends far beyond simple rotational support. By reducing friction, handling diverse loads, minimizing vibration, and maintaining precision, rolling bearings enhance the efficiency, reliability, and lifespan of countless mechanical systems.
Conclusion
The metal rolling bearing remains a cornerstone of modern industrial machinery, providing critical support for rotating and oscillating components across a wide range of applications. From basic ball bearing and roller bearing types to specialized spherical roller and tapered roller bearings, the industry offers solutions tailored to varying load capacities, speed requirements, and environmental conditions. High-precision metal rolling bearing, lubricated bearings for high-speed machinery, and corrosion-resistant stainless steel bearings represent the forefront of current technological and functional innovation.
For engineers and procurement specialists, careful consideration of load capacity, lubrication type, misalignment tolerance, and durability is essential when selecting the right bearing for each application. Leveraging functional comparisons and understanding long-tail application requirements can optimize performance, reduce maintenance costs, and improve operational efficiency.
News categories
Exhibition Information
Product categories
Contact
 1st Floor, Building 4, East Side, Jinger Road, Yuxin Town, Nanhu District, Jiaxing City, Zhejiang Province, China
1st Floor, Building 4, East Side, Jinger Road, Yuxin Town, Nanhu District, Jiaxing City, Zhejiang Province, China
 [email protected][email protected]
[email protected][email protected]
 +86-137 0583 8919+86-135 8638 0656
+86-137 0583 8919+86-135 8638 0656
Copyright © Jiaxing Lanyue Metal Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Custom High-Performance Industrial Fasteners Manufacturers, Suppliers
 English
English  Español
Español  Deutsch
Deutsch